PAEDIATRIC ASSESSMENT
At Golden Ears Audiology Clinic, We provide Paediatric testing for children over the age of 3 years.
BOOK APPOINTMENTDid you know?
The following are signs of hearing loss in children:
– Delayed speech development
– Do not respond when you call them
– Struggling to hear in the classroom and a drop in school performance
– Withdrawal from other children and prefer to play alone
– Poor concentration
– Change in their behaviour such as tiredness or frustration
– Constant ear infections
– Turn the TV louder than the rest of the family
We offer Low competitive prices at £69 for Paediatric Assessment with FREE video Otoscopy.
Frequently Asked Questions
Does my child need a hearing test?
If you child is showinng signs of hearing loss discussed on the Left side, they may need a hearing test.
Do you remove ear wax for children at Golden Ears?
We offer microsuction for children at our clinic. Please contact us to discuss your requirements.
What tests do you offer for paediatric assessment?
We offer Video otoscopy, Play audiometry, Speech testing, Tympanometry, Acoustic reflex testing and Otoacoustic emissions testing.
What is play Audiometry?
This involves conditioning a child to engage in a play task such as putting men in a boat, building a tower etc when a sound is introduced through headphones, to measure their hearing levels.
What is tympanometry and what information does it give?
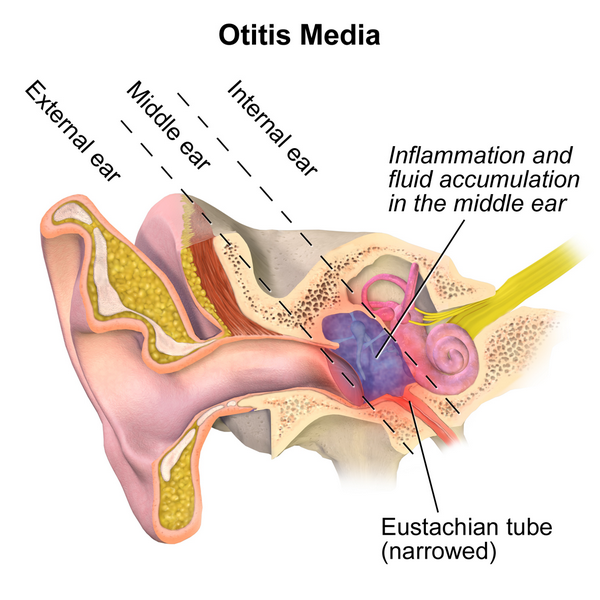
Tympanometry assists in ruling out middle ear pathology. Children below the ages of 5 years are prone to suffer from otitis media. The test takes less than 1 minute on a cooperative child. A soft probe is inserted in the ear canal to record the movement of the ear drum when pressure is changed in the ear canal.
What is an Otoacoustic emission test?
The purpose of an otoacoustic test is to determine the status of the outer hair cells. It is a sensitive test of hearing compared to a hearing test.